SUMMARY: Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women in the US and about 1 in 8 women (12%) will develop invasive breast cancer during their lifetime. Approximately 266,120 new cases of invasive breast cancer will be diagnosed in 2018 and about 40,920 women will die of the disease. Approximately 70% of breast tumors express Estrogen Receptors and/or Progesterone Receptors and these patients are often treated with anti-estrogen therapy as first line treatment. However, resistance to hormonal therapy occurs in a majority of the patients.
Cyclin Dependent Kinases (CDK) play a very important role to facilitate orderly and controlled progression of the cell cycle. Genetic alterations in these kinases and their regulatory proteins have been implicated in various malignancies. Cyclin Dependent Kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4 and CDK6) phosphorylate RetinoBlastoma protein (RB), and initiate transition from the G1 phase to the S phase of the cell cycle. RetinoBlastoma protein has antiproliferative and tumor-suppressor activity and phosphorylation of RB protein nullifies its beneficial activities. CDK4 and CDK6 are activated in hormone receptor positive breast cancer, promoting breast cancer cell proliferation. Further, there is evidence to suggest that endocrine resistant breast cancer cell lines depend on CDK4 for cell proliferation. The understanding of the role of Cyclin Dependent Kinases in the cell cycle, has paved the way for the development of CDK inhibitors.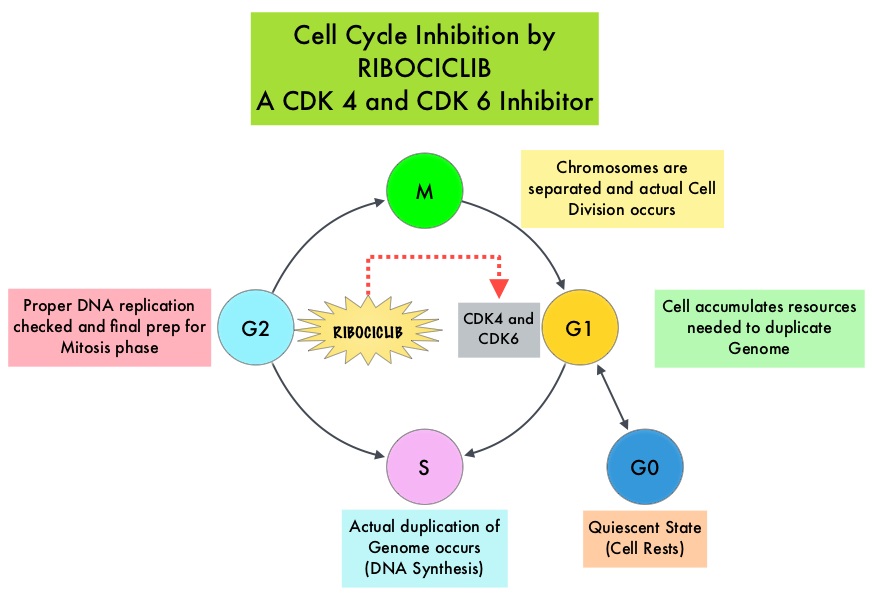
KISQALI® (Ribociclib) is an orally bioavailable, selective, small-molecule inhibitor of CDK4/6 that blocks the phosphorylation of RetinoBlastoma protein, thereby preventing cell-cycle progression and inducing G1 phase arrest. KISQALI® in combination with an Aromatase Inhibitor has been approved by the FDA for pre and perimenopausal women with HR (Hormone Receptor)-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer, as initial endocrine-based therapy. The efficacy of KISQALI® was evaluated in two prior randomized phase III studies. In the MONALEESA-2 trial which evaluated KISQALI® in combination with FEMARA® (Letrozole) compared to FEMARA® alone, in postmenopausal women with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer who received no prior therapy for their advanced breast cancer, the addition of KISQALI® to FEMARA® significantly prolonged Progression Free Survival (PFS) compared to FEMARA® alone. In the MONALEESA-7 study, KISQALI® in combination with Tamoxifen or a Non-Steroidal Aromatase Inhibitor plus ZOLADEX® (Goserelin) was compared with Tamoxifen or an Aromatase Inhibitor plus ZOLADEX®, in premenopausal or perimenopausal women with HR-positive, HER2- negative advanced breast cancer, who had not previously received endocrine therapy for advanced disease. In this study of premenopausal women, KISQALI® plus endocrine therapy significantly improved PFS compared with placebo plus endocrine therapy
MONALEESA-3 is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase III study which compared the efficacy of KISQALI® in combination with FASLODEX® with FASLODEX® alone, among postmenopausal women with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer who received no prior or only one line of prior endocrine therapy for advanced disease. In this trial, 726 women were randomized, of whom 367 were treatment-naïve and 345 patients had received up to one line of prior endocrine therapy for advanced disease. . Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive KISQALI® plus FASLODEX® (N=484) or placebo plus FASLODEX® (N=242). Treatment consisted of KISQALI® 600 mg orally daily 3 weeks on and 1 week off and FASLODEX® 500 mg IM on day 1 of each 28-day cycle, with an additional dose given on day 15 of cycle 1. Patients were stratified by the presence or absence of lung or liver metastases and prior endocrine therapy (first-line versus second-line). The median age in both groups was 63 years. The Primary endpoint was Progression Free Survival. Secondary end points included Overall Survival, Overall Response Rate, and Safety. The median time from randomization to data cutoff was 20.4 months.
Among all randomized patients, the median PFS in the KISQALI® plus FASLODEX® group was 20.5 months compared to 12.8 months in the FASLODEX® plus placebo group (HR= 0.59; P<0.001). This represented a 41% reduction in the risk of disease progression. The PFS benefit was consistent among the 367 patients who were treatment-naïve (HR=0.57) and 345 patients had received up to one line of prior endocrine therapy for advanced disease (HR=0.56). In the subgroup of patients taking KISQALI® plus FASLODEX® as first-line treatment, the median PFS was not reached and 70% were estimated to remain Progression Free at median follow up of 16.5 months. Among those patients with measurable disease at baseline, the Overall Response Rate was 40.9% for the KISQALI® plus FASLODEX® arm versus 28.7% for FASLODEX® plus placebo group (P=0.003). At first interim analysis, the Overall Survival data were immature. The most common grade 3/4 Adverse Events in patients receiving KISQALI® plus FASLODEX® compared to FASLODEX® alone were neutropenia (53.4% versus 0%) and leukopenia (14.1% versus 0%).
It was concluded that KISQALI® plus FASLODEX® might represent a new, first or second-line treatment option for patients with Hormone Receptor-positive, Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer. MONALEESA-3 is the only randomized Phase III trial to study a CDK4/6 inhibitor plus FASLODEX® in the first-line setting, with demonstrable efficacy in patients with de novo advanced breast cancer and those who had not received adjuvant therapy in more than a year. Ribociclib (RIB) + fulvestrant (FUL) in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive (HR+), HER2-negative (HER2 –) advanced breast cancer (ABC): Results from MONALEESA-3. Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia SKL, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2018: 36, (suppl; abstr 1000).

