SUMMARY: The FDA on January 18, 2017 granted accelerated approval to IMBRUVICA® (Ibrutinib) for the treatment of patients with Marginal Zone Lymphoma (MZL), who require systemic therapy and have received at least one prior anti-CD20 based therapy. The American Cancer Society estimates that in 2017, about 72,240 people will be diagnosed with Non Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) in the United States and about 20,140 individuals will die of this disease. Indolent Non Hodgkin Lymphomas are mature B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders and include Follicular Lymphomas, Small Lymphocytic Lymphomas (SLL), LymphoPlasmacytic Lymphomas (LPL) and Marginal Zone Lymphoma subtypes such as Nodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma (NMZL), Extranodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma (ENMZL)/Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) lymphoma and Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma (SMZL). Marginal Zone Lymphoma is an indolent B-cell lymphoma originating in the lymph nodes as well as in organs including the stomach, salivary glands, thyroid gland, lungs and spleen. It accounts for approximately 10% of all cases of Non Hodgkin Lymphomas (NHL) in adults and is often linked to chronic infection. When treatment is indicated, patients are often treated with a RITUXAN® (Rituximab) based regimens with improved outcomes. Relapses however are common and there is presently no therapy, specifically approved for the treatment of Marginal Zone Lymphoma.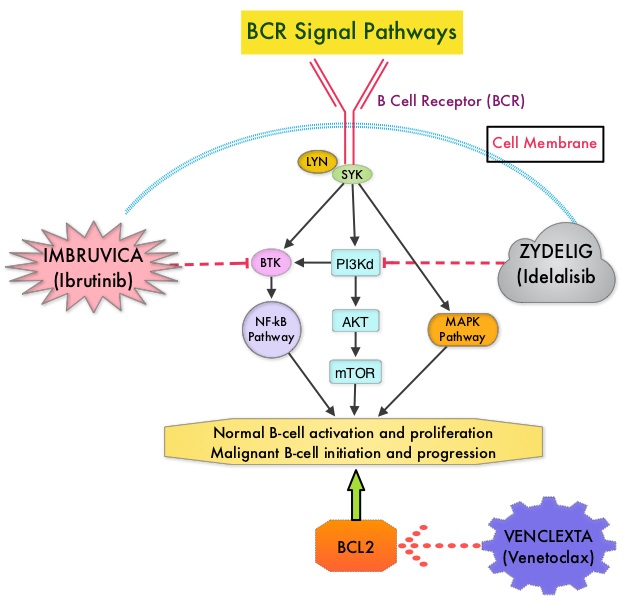
Normal B-cell activation and proliferation is dependent on B-Cell Receptor (BCR) signaling. This signaling is also important for initiation and progression of B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) is a member of the Tec family of kinases, downstream of the B-cell receptor and is predominantly expressed in B-cells. It is a mediator of B-cell receptor signaling in normal and transformed B-cells. Following binding of antigen to the B-Cell Receptor, kinases such as Syk (Spleen Tyrosine Kinase), Lyn (member of the Src family of protein tyrosine kinases) and BTK (Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase) are activated, with subsequent propagation through PI3K/Akt, MAPK, and NF-κB pathways. This results in B-cell activation and proliferation. IMBRUVICA® (Ibrutinib) is an oral, irreversible inhibitor of BTK and inhibits cell proliferation and promotes programmed cell death (Apoptosis) by blocking B-cell activation and signaling. IMBRUVICA® is presently approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/ Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma including those with del-17p, patients with Mantle Cell Lymphoma who had received at least one prior therapy, and patients with Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia.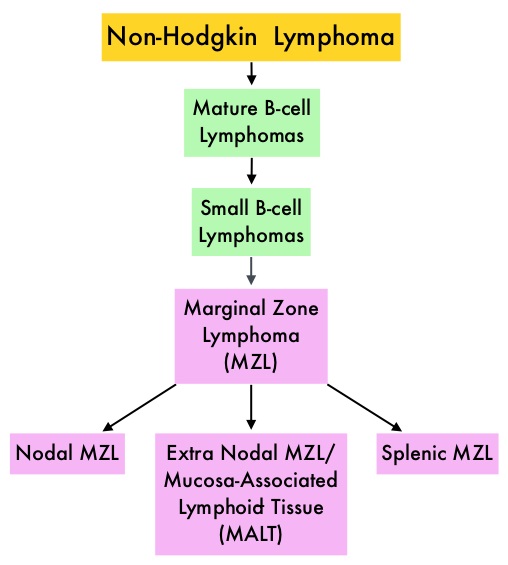
The approval of IMBRUVICA®, in MZL was based on results from a multicenter, open-label, single-arm, phase II trial, in which the safety and efficacy of IMBRUVICA® was evaluated in 63 patients with Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Enrolled patients had previously received one or more prior therapies including at least one anti-CD20 targeted monoclonal antibody -containing regimen or monotherapy RITUXAN®. The subtypes of Marginal Zone Lymphomas included, Extra Nodal MZL (N=32), Nodal MZL (N=17) and Splenic MZL (N=14). The median number of prior systemic therapies was 2 and 35% of the enrolled patients had 3 or more prior therapies. Treatment consisted of IMBRUVICA® 560 mg orally once daily until progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary study endpoint was Overall Response Rate (ORR). Secondary endpoints included Duration of Response (DOR), Progression Free Survival (PFS), Overall Survival (OS), and safety.
The Overall Response Rate as assessed by an independent review committee was 46%,of whom with 3.2% of patients had a Complete Response and 42.9% achieved a Partial Response. This benefit was observed across all three subtypes of Marginal Zone Lymphomas (Overall Response Rate was 46.9%, 41.2%, and 50.0% for ENMZL/MALT, NMZL, and SMZL subtypes, respectively). The median time to response was 4.5 months and the median duration of response was not reached (range, 16.7 months – Not Reached). The most common adverse events were fatigue, diarrhea, cytopenias, nausea, peripheral edema, cough, arthralgia and dyspnea.
The authors concluded that single agent IMBRUVICA® achieved high Response Rates and durable responses in patients with Relapsed/Refractory Marginal Zone Lymphoma. IMBRUVICA® addresses an unmet need for previously treated Marginal Zone Lymphoma patients, who are in need of non-chemotherapy treatment options. Single-Agent Ibrutinib Demonstrates Efficacy and Safety in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Marginal Zone Lymphoma: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase 2 Study. Noy A, de Vos S, Thieblemont C, et al. Presented at: ASH 2016 Annual Meeting and Exposition. Abstract 1213.

