SUMMARY: Cancer mortality rates in the United States have declined 20% from their peak of 215 per 100,000 in 1991 to 172 per 100,000 in 2010. With more than half a million Americans diagnosed with cancer each year, recent advances in cancer treatment and research has lead to improved survival and better quality of life, with 14.5 million cancer survivors alive in the US today. This Annual Report on Progress Against Cancer explored the clinical advances of the prior year (2014), that made the greatest impact on improving cancer care. This report was developed based on research published in peer-reviewed scientific and medical journals and information presented at major scientific meetings over a one year period between October 2013 to September 2014. A brief summary of this report (Part I) is presented. Part I includes, ADVANCE OF THE YEAR and ADVANCES IN PREVENTION AND SCREENING. Clinical trial details for several of these studies can be accessed at www.oncoprescribe.com
ADVANCE OF THE YEAR – TREATMENT OF CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) is the most common form of adult leukemia and is more common in the elderly. Four new therapies associated with fewer toxicities compared with standard therapy, were recently approved for patients with CLL.
Two Effective Treatment Options for Patients with Newly Diagnosed CLL
GAZYVA® (Obinutuzumab) is a fully humanized, third generation, type II, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody that selectivity binds to the extracellular domain of the CD20 antigen on malignant human B cells. In a phase III trial involving 589 treatment naïve CLL patients, GAZYVA® in combination with LEUKERAN® (Chlorambucil) more than doubled the Progression Free Survival (PFS) from 11.1 months with LEUKERAN® alone to 26.7 months (HR=0.18, P<0.001). The combination of GAZYVA® and LEUKERAN® also prolonged Overall Survival (OS) when compared to LEUKERAN® alone (HR=0.41; P=0.002). This benefit however was not noted with the RITUXAN® plus LEUKERAN® combination. Treatment with GAZYVA® plus LEUKERAN® when compared with RITUXAN® plus LEUKERAN® resulted in a longer PFS (26.7 vs15.2 months; HR=0.39; P<0.001), higher complete response rates (20.7% vs 7.0%) and deeper molecular responses.
ARZERRA® (Ofatumumab), a second generation fully human IgG 1 monoclonal antibody, which targets a different region (different epitope) of the CD20 molecule in combination with LEUKERAN®, was compared with LEUKERAN® alone, as first line treatment in a study involving 447 CLL patients. The median PFS was 22.4 months for patients receiving ARZERRA® in combination with LEUKERAN® compared with 13.1 months for those receiving single agent LEUKERAN® (HR=0.57, P< 0.001). The Objective Response Rate was higher with the combination regimen versus single agent LEUKERAN® (82% vs 69%, P=0.001).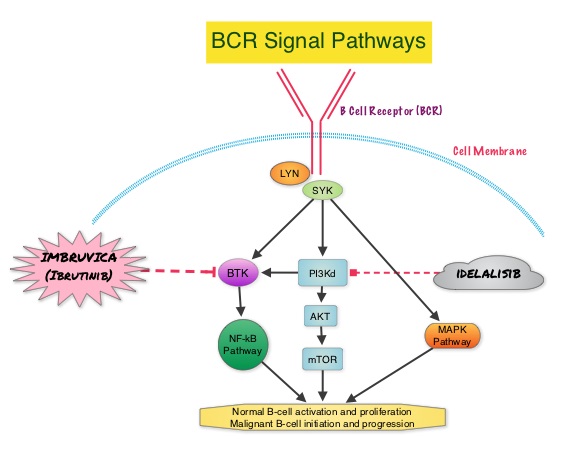
Two New Non-Chemotherapy Alternatives for Relapsed and Treatment-Resistant CLL
IMBRUVICA® (Ibrutinib) is an oral, irreversible inhibitor of BTK and inhibits cell proliferation and promotes programmed cell death (Apoptosis). IMBRUVICA® was compared to single agent ARZERRA® in a phase III trial involving 391 patients with relapsed CLL. Thirty percent (30%) of the patients had deletion of chromosome 17p. At a median follow up of 9.4 months, IMBRUVICA® significantly prolonged PFS compared to ARZERRA® (median not reached vs 8.1 months; HR 0.215, P<0.0001) with a 78.5% reduction in the risk of disease progression and also significantly improved OS (median not reached, HR 0.43, P=0.0049) when compared with ARZERRA®, with a 57% reduction in the risk of death.
In a phase III study involving 220 previously treated patients with recurrent CLL, ZYDELIG® (Idelalisib), a highly selective oral inhibitor of the enzyme PhosphoInositide 3-Kinase (PI3K) that specifically blocks the delta isoform of PI3K enzyme and its signaling pathway, was combined with RITUXAN® and compared with placebo given along with RITUXAN®. The median PFS with ZYDELIG® in combination with RITUXAN® was significantly prolonged compared with Placebo and RITUXAN® (10.7 months vs 5.5 months). An improvement in the Overall Survival (OS) was also noted in the ZYDELIG® group compared with patients in the RITUXAN® and placebo group (HR = 0.28; P = 0.018).
ADVANCES IN PREVENTION AND SCREENING
Breast Cancer Prevention
The only two drugs currently approved by the FDA to prevent breast cancer are NOLVADEX® (Tamoxifen) and EVISTA® (Raloxifene). These agents block the estrogen receptors and can be used in both pre and postmenopausal women. NOLVADEX® is however associated with thromboembolic evens as well as endometrial carcinoma. ARIMIDEX® (Anastrozole), an Aromatase Inhibitor (AI), in a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial, involving 3864 women at increased risk of breast cancer, reduced this risk of breast cancer by 53% compared to placebo, over a 5-year period (P<0.0001), in post-menopausal women. This benefit with ARIMIDEX® was accomplished without increase in the risk of heart attacks or fractures, compared with placebo. There was however increase in the incidence of joint and muscle pain as well as hot flushes and night sweats. Another AI, AROMASIN® (Exemestane) in a previously published study (MAP.3 trial) significantly reduced the incidence of all breast cancers by 53% and invasive breast cancers by 65%, after a median follow up of 3 years.
Screening for Lung Cancer
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommended annual screening for lung cancer with Low Dose Computed Tomography in adult individuals, between ages 55 to 80 years who have a 30 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years. Screening should be discontinued once a person has not smoked for 15 years or develops a health problem that substantially limits life expectancy or the ability or willingness to have curative lung surgery. The use of Low Dose CT (LDCT) scans for 3 years in this high risk, healthy patients, resulted in a 20% reduction in Lung cancer mortality, compared to screening with a chest X-Ray in the NCI-sponsored National Lung Screening Trial (NLST).
Masters GA, Krilov L, Bailey HH, et al. Published online before print January 20, 2015, doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.59.9746

