SUMMARY: The American Cancer Society estimates that about 62,700 new cases of kidney cancer will be diagnosed in the United States in 2016 and over 14,000 patients will die from this disease. The prognosis for patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) is dependent on the stage of disease and risk factors. Two validated models, the University of California Los Angeles Integrated Staging System (UISS) and the Stage, Size, Grade, and Necrosis (SSIGN) score were developed, to assess the risk for relapse. UISS is based on ECOG Performance Status, Fuhrman nuclear grading and TNM pathological stage, whereas the SSIGN score takes Stage, Size, Grade and Necrosis into consideration. Approximately 16% of patients with RCC present with Locoregional disease, and up to 40% of these patients relapse with metastatic disease, following nephrectomy. The 5-year survival for locoregional (stage III) disease is 53%, and 8% for metastatic disease. The standard management of high risk patients following nephrectomy has been surveillance, as there has been limited data demonstrating the benefit of adjuvant therapy in reducing the risk of relapse.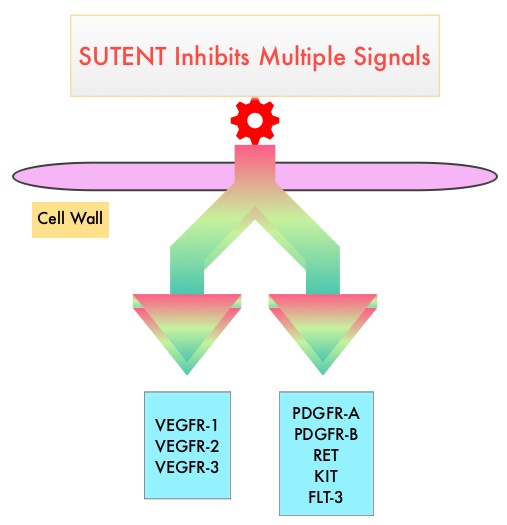
SUTENT® (Sunitinib) is a MultiKinase Inhibitor (MKI) which simultaneously targets the tumor cell wall, vascular endothelial cell wall as well as the pericyte/fibroblast/vascular/ smooth vessel cell wall and is capable of specifically binding to tyrosine kinases, inhibiting the earlier signaling events and thereby inhibits phosphorylation of VEGF receptor, PDGF receptor, FLT-3 and c-KIT. SUTENT® is indicated for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma and in a multi-center, randomized study, demonstrated superior Progression Free Survival and Objective Response Rate, when compared with Interferon Alfa, in patients with treatment-naïve Renal Cell Carcinoma. The authors in this study examined the efficacy and safety of SUTENT® in patients with locally advanced RCC, at high risk for tumor recurrence, following nephrectomy.
Sunitinib as Adjuvant Treatment for Patients at High Risk of Recurrence of Renal Cell Carcinoma Following Nephrectomy (S-TRAC) is a randomized, double blind, phase III trial in which 615 patients with locoregional, high risk, clear cell Renal Cell Carcinoma were randomly assigned to receive SUTENT® (N=309) or placebo (N=306). Treatment consisted of either SUTENT® 50 mg PO daily or placebo, on a 4-weeks-on, 2-weeks-off schedule, for 1 year or until disease recurrence or unacceptable toxicity. Eligible patients had tumor Stage III or higher, regional lymph node metastasis, or both and were required to have absence of macroscopic residual or metastatic disease after nephrectomy, as confirmed by a CT scan. The primary end point was Disease Free Survival and secondary end points included Overall Survival, and Safety.
It was noted that the median duration of Disease Free Survival was 6.8 years in the SUTENT® group and 5.6 years in the placebo group (HR=0.76; P=0.03). Overall Survival data were not mature at the time of this analysis. Grade 3 or 4 adverse events were more frequent in the SUTENT® group compared to the placebo group and dose reductions, dose interruptions and discontinuations were more frequent in the SUTENT® group as well. The most commonly reported adverse events were skin toxicity (palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia), hypertension, and fatigue, with declines in quality of life while on active therapy. In a previously published adjuvant trial (ASSURE trial), there was no improvement in Disease Free Survival in patients receiving Sunitinib or Sorafenib as compared with placebo. This has been attributed to the ASSURE trial including many patients with early (Stage 1) tumors as well as those with non-clear cell histology. Additionally, the dosing schedule in the ASSURE trial was lower than this present study.
It was concluded that adjuvant treatment with SUTENT® following nephrectomy in patients with high risk disease, results in significantly improved Disease Free Survival but this benefit may be associated with higher rate of toxicities during treatment. Adjuvant Sunitinib in High-Risk Renal-Cell Carcinoma after Nephrectomy. Ravaud A, Motzer RJ, Pandha HS, et al. for the S-TRAC Investigators. October 10, 2016DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1611406

