SUMMARY: The American Society for Clinical Oncology (ASCO) after careful review, endorsed the Society for Integrative Oncology (SIO) guideline on the use of integrative therapies during and after breast cancer treatment. Integrative medicine is defined as a patient-centered, evidence-informed field of care that uses mind and body practices, natural products, and/or lifestyle modifications to improve health, quality of life, and clinical outcomes. The ASCO Expert Panel determined that the recommendations in the SIO guideline published in 2017 are clear, thorough, and based on the most relevant scientific evidence. The panel emphasized that these therapies are complementary and should be used along with conventional anticancer treatment, thereby taking a more comprehensive treatment approach across the cancer care continuum, to manage symptoms and adverse effects of breast cancer treatment. This ASCO guideline excluded lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, mainstream interventions such as support groups, and practices like attention-restoration therapy, that are still being evaluated. Practices such as prayer and spirituality were not considered specifically integrative oncology therapy.
Guideline Question
What are evidence-based approaches to the use of integrative therapies in the management of symptoms and adverse effects during and after breast cancer treatment?
Target Population
Patients undergoing treatment of breast cancer and survivors of breast cancer
Target Audience
Oncologists, integrative medicine providers, supportive care specialists, nurses, pharmacists, primary care providers, and patients with breast cancer
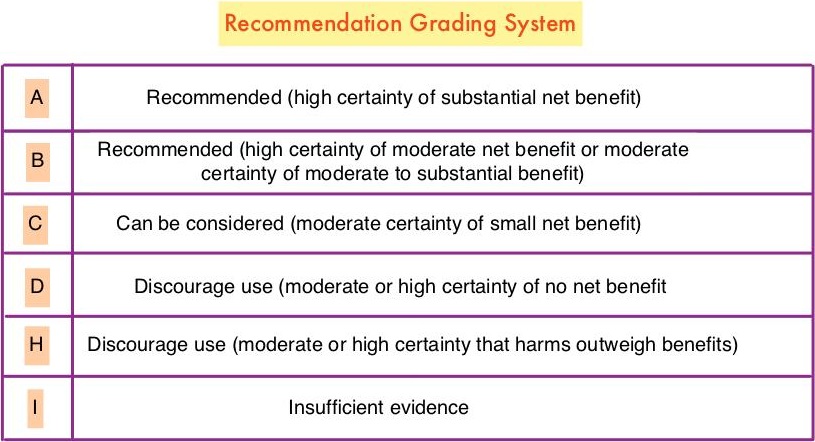
Key Recommendations
Acute Radiation Skin Reaction
Aloe vera and hyaluronic acid cream should not be recommended for improving acute radiation skin reaction. (Grade D)
Anxiety and Stress Reduction
Meditation is recommended for reducing anxiety. (Grade A)
Music therapy is recommended for reducing anxiety. (Grade B)
Stress management is recommended for reducing anxiety during treatment, but longer group programs are likely better than self-administered home programs or shorter programs. (Grade B)
Yoga is recommended for reducing anxiety. (Grade B)
Acupuncture, massage, and relaxation can be considered for reducing anxiety. (Grade C)
Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting
Acupressure can be considered as an addition to antiemetic drugs to control nausea and vomiting during chemotherapy. (Grade B)
Electroacupuncture can be considered as an addition to antiemetic drugs to control vomiting during chemotherapy. (Grade B)
Ginger and relaxation can be considered as additions to antiemetic drugs to control nausea and vomiting during chemotherapy. (Grade C)
Glutamine should not be recommended for improving nausea and vomiting during chemotherapy. (Grade D)
Depression and Mood Disturbance
Meditation, particularly mindfulness-based stress reduction, is recommended for treating mood disturbance and depressive symptoms. (Grade A)
Relaxation is recommended for improving mood disturbance and depressive symptoms. (Grade A)
Yoga is recommended for improving mood disturbance and depressive symptoms. (Grade B)
Massage is recommended for improving mood disturbance. (Grade B)
Music therapy is recommended for improving mood disturbance. (Grade B)
Acupuncture, healing touch, and stress management can be considered for improving mood disturbance and depressive symptoms. (Grade C)
Fatigue
Hypnosis and ginseng can be considered for improving fatigue during treatment. (Grade C)
Acupuncture and yoga can be considered for improving post-treatment fatigue. (Grade C)
Acetyl-l-carnitine and guarana should not be recommended for improving fatigue during treatment. (Grade D)
Lymphedema
Low-level laser therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, and compression bandaging can be considered for improving lymphedema. (Grade C)
Neuropathy
Acetyl-l-carnitine is not recommended for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with breast cancer due to potential harm. (Grade H)
Pain
Acupuncture, healing touch, hypnosis, and music therapy can be considered for the management of pain. (Grade C)
Quality of Life
Meditation is recommended for improving quality of life. (Grade A)
Yoga is recommended for improving quality of life. (Grade B)
Acupuncture, mistletoe, qigong, reflexology, and stress management can be considered for improving quality of life. (Grade C)
Sleep Disturbance
Gentle yoga can be considered for improving sleep. (Grade C)
Vasomotor/Hot Flashes
Acupuncture can be considered for improving hot flashes. (Grade C)
Soy is not recommended for hot flashes in patients with breast cancer due to lack of effect. (Grade D)
Integrative Therapies During and After Breast Cancer Treatment: ASCO Endorsement of the SIO Clinical Practice Guideline. Lyman GH, Greenlee H, Bohlke K, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:2647-2655

